If you live in Boise, Idaho and you’re wondering about the quality and safety of your drinking water, you’re not alone. Drinking water quality is an important issue for homeowners, if you live in an area with hard water. Many people ask – Does Boise have hard water.
Boise tap water has an average hardness of 108 ppm. This is considered moderately hard according to the USGS water hardness measures. Boise’s drinking water is hard because they get their water from an underground aquifer where the water picks up calcium and magnesium as it travels through the ground. While hard water is generally safe to drink, it can cause issues with soap scum, scale buildup, and appliance damage.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the relative hardness of Boise’s drinking water and explore the various treatments available to soften your drinking water and a lot more.
Read my article about water hardness in other cities.
Table of Contents
Does Boise Have Hard Water?

Yes, Boise has moderately hard water. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), Boise water has a hardness of 108 milligrams per liter (mg/L), which is the same as 108 parts per million (ppm). When converted to grains per gallon (gpg), Boise’s water hardness is 6.3 gpg.
The USGS classifies water with a hardness between 60 and 120 ppm as moderately hard. With a hardness of 108 ppm, Boise’s water falls within this range. Hard water is not harmful to human health, but it can cause some problems.
| City | Average Hardness Calcium Carbonate (mg/L) | Average Hardness (grains per gallon) | Zip Code |
| Boise | 108 ppm | 6 gpg | 83702 | 83703 | 83704 | 83705 | 83706 | 83709 | 83712 | 83713 | 83716 |
| Couer d’Alen | 127 ppm | 7 gpg | 83814 | 83815 |
| Idaho Falls | 239 ppm | 4 gpg | 83401 | 83402 | 83404 | 83406 |
| Kimberly | 142 ppm | 8 gpg | 83341 |
| Kuna | 137 ppm | 8 gpg | 83634 | 83642 | 83687 |
| Lewiston | 17 ppm | 1 gpg | 83501 |
| Meridian | 106 ppm | 6 gpg | 83616 | 83642 | 83634 | 83646 | 83713. |
| Moscow | 110 ppm | 6 gpg | 83843 | 83844 |
| Nampa | 66 ppm | 4 gpg | 83651 | 83686 | 83687 |
| Pocatello | 350 ppm | 20 gpg | 83201 | 83202 | 83204 | 83209 |
Learn about water hardness in these cities:
Does Portland Have Hard Water?
Does Washington CD have hard water?
Idaho Water Hardness
Idaho is known for its pristine wilderness, including its abundant rivers, lakes, and streams. The state gets its drinking water from both surface water sources, such as rivers and lakes, and groundwater sources, such as aquifers.
When it comes to water hardness, Idaho’s water quality can vary depending on the source of the water. According to the USGS, the water hardness in Idaho ranges from soft to very hard, with the highest levels of hardness typically found in areas with high mineral content, such as the eastern part of the state.
For example, in the city of Pocatello in eastern Idaho, the water hardness can range from 130 to 250 ppm, which is considered very hard. On the other hand, in the city of Boise in western Idaho, the water hardness is considered moderately hard, with a hardness of 108 ppm.
Check out this video about water treatment for Boise’s tap water.
What is Hard Water?
Hard water is water that contains high levels of dissolved minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and sometimes iron. These minerals are picked up as water travels through rock and soil, and are harmless to human health, but can cause a number of problems around the home.
The USGS rates water hardness on a scale from soft to very hard, based on the concentration of dissolved minerals in the water.
The following table shows the classification of water hardness and the corresponding concentrations of minerals in parts per million (ppm).
| Classification | Hardness (ppm) |
| Soft | 0 – 60 |
| Moderately Hard | 60 – 120 |
| Hard | 120 – 180 |
| Very Hard | Over 180 |
What are the Problems Caused by Hard Water?
Hard water can cause several problems around the home, including:
- Soap scum and residue: Hard water can make it difficult to get soap to lather, which can lead to soap scum buildup on shower walls, bathtubs, and other surfaces.
- Scale buildup: Over time, the minerals in hard water can accumulate in pipes, water heaters, and appliances, reducing their efficiency and lifespan.
- Stains and discoloration: Hard water can cause stains and discoloration on sinks, toilets, and other surfaces, making them difficult to clean.
- Dry skin and hair: Hard water can also dry out skin and hair, leaving them feeling itchy and brittle.
Who is Boise’s Water Provider?
The City of Boise water provider is a French-owned corporation called Veolia (formerly SUEZ). They serve over 120,000 people and households in the area.
They are regulated by the Idaho Public Utilities Commission, which sets the rates the company can charge, defines the boundary of their service area, and decides whether they can acquire other providers. Boise’s water is also regulated by the Idaho Department of Environmental Quality, just like a public utility.
Where does Boise Water Come From?
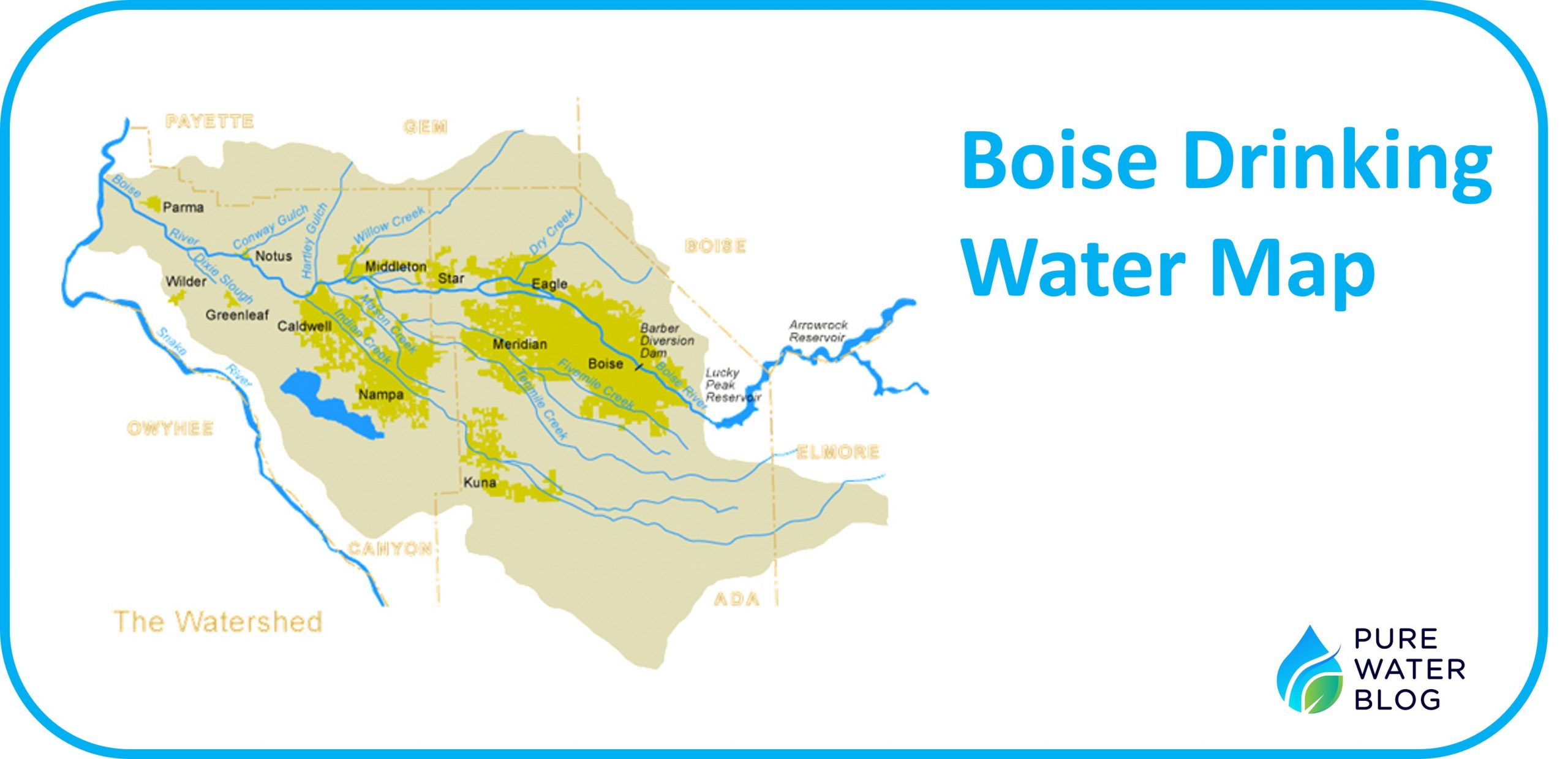
Boise’s water supply comes from a combination of surface water and groundwater sources. According to the Veolia, Boise gets about 80% of its drinking water from 83 wells in the Boise Valley Aquifer. The rest comes from surface water sources, including the Boise River and Lucky Peak Reservoir.
Is Boise’s Tap Water Treated?
Yes, Boise’s tap water is treated to ensure its safety and quality.
Tap water undergoes various treatment processes, depending on the source.
Groundwater, obtained from wells, is treated with a small amount of chlorine to eliminate any potential harmful microorganisms. Additionally, low doses of polyphosphate are added to 9 wells to isolate iron and manganese and to maintain water clarity.
Surface water, taken from the Boise River, undergoes treatment at two plants:
- The Marden Water Treatment Plant: this facility uses an upflow clarification process and conventional filtration to eliminate particulate matter.
- The Columbia Water Treatment Plant: this water is treated at a membrane plant that uses microfiltration to remove particulate matter.
After filtration, chlorine is added to destroy harmful bacteria, and pH adjustment is used to reduce water corrosivity.
Quality of Boise Tap Water
Boise’s tap water is generally considered to be safe and of high quality. The city’s Public Works Department regularly tests the water to ensure that it meets or exceeds all federal and state drinking water standards. However, there have been some contamination issues in the past, including:
- Elevated levels of lead in some homes due to old lead pipes or fixtures.
- Occasional high levels of disinfectant byproducts (DBPs), which can form when chlorine interacts with organic matter in the water.
- Trace amounts of contaminants such as arsenic, nitrate, and radionuclides have also been detected in some areas, but these levels are typically below the maximum allowable limits set by federal and state agencies.
How Much Water Does Boise Use Each Year?
According to the City of Boise’s 2021 Water Quality Report, the city uses an average of 26.8 million gallons of water per day (MGD). This equates to approximately 9.8 billion gallons of water per year.
Idaho Water Use and Consumption in Statistics
Idaho is one of the top 10 states in the United States for water consumption, with an annual average of 10.6 billion gallons of water used each day. The majority of the state’s water is used for agricultural purposes, with irrigation accounting for over 80% of the state’s total water use.
In addition to agricultural use, Idaho’s water is also used for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes. In 2015, the Idaho Department of Water Resources estimated that 85% of the state’s population was served by public water systems, with the remaining 15% relying on private wells or other sources.
What Can I Do About Hardness in My Water?
If you’re concerned about the hardness of your water, there are several things you can do to address the issue. Here are some options to consider:
Install a water softener
Water softeners are the most common and effective solution for hard water. They work by using ion exchange to remove the minerals that cause hardness and replacing them with sodium or potassium ions. While this can be effective in reducing the hardness of your water, it’s important to note that it can also increase your sodium intake and may not be the best option for people on low-sodium diets.
Use a Chemical water conditioner
Chemical water conditioners are another option for addressing hardness. These products work by adding chemicals to the water that prevent the minerals from sticking to surfaces and forming scale. While these products can be effective, they may not be as long-lasting as other solutions and may require ongoing maintenance.
Purchase bottled water
If you’re concerned about the quality of your tap water, you may consider purchasing bottled water for drinking and cooking. However, it’s important to note that bottled water can be expensive and can create a lot of plastic waste.
Conclusion
If you are a homeowner in Boise concerned about the hardness of your tap water, it’s important to understand that the city’s water supply is moderately hard. This hardness is due to the natural mineral content in the region’s water sources, which are mainly surface water from the Boise River and groundwater from local wells.
Fortunately, there are several solutions available to address hard water, such as installing a water softener or using a chemical water conditioner.

