When it comes to drinking water, safety is always a top concern. We all want to make sure that the water we drink is free of harmful contaminants and chemicals. That’s why many people turn to Brita filters as a way to improve the quality of their drinking water. But what does a Brita filter remove? And is your drinking water safe?
In this blog post, we will answer all of your questions about Brita filters and help you decide if they are right for you!
You may be interested in my article – What Does Brita Not Filter Out? 11 Contaminants That Could Be in Your Drinking Water!
Table of Contents
Brita Filters
Brita is a popular brand of water filter that is used in many households across the country. These filters are designed to remove impurities from your water, such as chlorine, lead, and other contaminants.
All about Brita
Brita was founded in Germany by Heinz Hankammer in 1966. The company obtained its first patent for residential water filtration in the 1970s.
In 2000, the Clorox Company acquired the sole rights to the Brita brand in the Americas. Today, all Brita products sold in the US are made by Clorox.
Type of filters Brita makes

Brita makes a range of filters for use in both residential and commercial settings. The most popular type of Brita filter is the Pitcher Filter, which is designed for use in the home.
Brita also makes a Faucet Mount Filter, as well as a bottle filter. In addition, the company offers a line of filters for commercial coffee makers.
The primary types of filters made by Brita for use in the home are:
- pitcher filter – These filters have a specially designed filter element that fits into a pitcher. Water is added to a reservoir on the top and flows via gravity through the filter media. Brita makes more than a dozen pitcher models and three filter sizes for this filter line.
- dispenser filter – The dispenser system from Brita is designed to provide filtered water on demand. The system has a filter that is located inside the dispenser unit and a separate reservoir for holding filtered water. These work like the pitcher filters but have a much greater storage capacity.
- faucet filter – This type of filter attaches to your kitchen faucet and filters the water as it is dispensed from the tap. The filter element screws onto the aerator and removes contaminants as you use the water.
- bottle filter – The bottle filter is a portable filter that can be used with the Brita water bottle. The filter element is inserted into the water bottle and removes contaminants as you drink.
Brita Filter Technology – How They Work
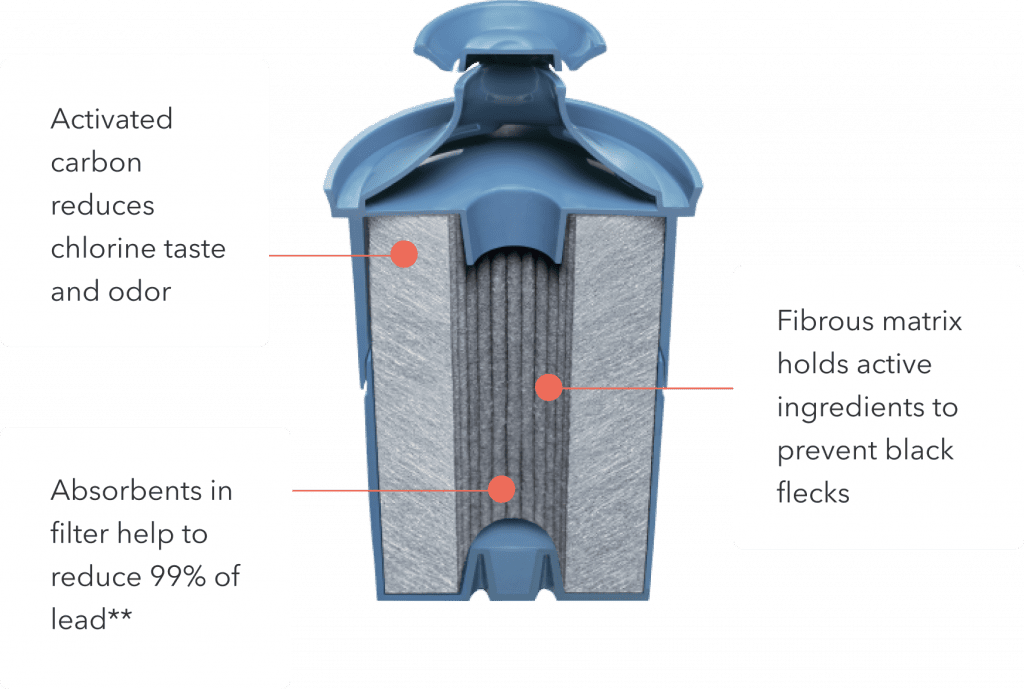
Brita filters use three different treatment technologies to purify your drinking water. These filtering methods include:
- particle filter
- activated carbon
- ion exchange resin
1 – Particle filter
Brita uses a particle filter to remove sediment, dirt, and rust from your water. This type of filter uses a process called mechanical filtration to trap contaminants in the filter media.
The particle filters used by Brita are made from layers of different materials, such as polypropylene and cellulose. The non-woven fibers in the filter media are designed to capture small solids but large enough to allow water to flow through.
As the water flows through the filter, suspended particles are trapped in the media and clean water is allowed to pass through. This filtration process is very effective at removing:
- silt
- sand and dirt
- rust
- asbestos fibers
- sediment
If your water has a lot of sediment and suspended solids, you may find that the filter becomes fouled sooner than normal. Brita recommends replacing the standard filter every 2 months and the LongLast+ every 6 months.
2 – Activated carbon filter

Activated carbon is a well-known and widely used water treatment technology. This type of filter uses a process called adsorption to remove contaminants from your water. Brita uses coconut shell activated carbon in their filters.
Adsorption is the process where molecules of a contaminant are attracted and bonded to the surface of the activated carbon filter media. As water flows through the filter, contaminants are trapped on the surface of the media and clean water is allowed to pass through.
Activated carbon filters are very effective at removing a wide range of contaminants, including:
- chlorine
- taste and odor compounds
- organic chemicals
- trihalomethanes (THMs)
The activated carbon removes substances that may impair taste, such as chlorine and chlorine compounds. It also removes lead and emerging contaminants such as PFAS.
3 – Ion exchange resin
Some Brita filters use ion exchange resin to remove heavy metals and other dissolved solids from your water. This type of filter uses a process called ion exchange to remove certain contaminants from your water.
Ion exchange is the process where the positively charged ions of the minerals and other impurities are attracted to and exchanged with the negatively charged ions of the resin media. As water flows through the filter, these unwanted compounds are trapped in the media and clean water is allowed to pass through.
Ion exchange resins are very effective at removing a wide range of contaminants, including:
- lead
- copper
- zinc
- cadmium
Contaminants Brita Filters Remove from Drinking Water
Brita filters are designed to remove a wide range of contaminants from your drinking water. The specific contaminants removed by each type of Brita filter are listed on the packaging.
As explained above, Brita offers several different types of filter systems to purify your drinking water. Depending on which type of filter system you have, your Brita will remove different contaminants.
Each of these filters uses a different combination of filtering technologies to remove contaminants. In the following section, we discuss how well each type of filter works at removing specific contaminants.
1 – Chlorine removal with Brita filters
Chlorine is used as a disinfectant in many public water supplies. It is relatively inexpensive, has the lowest production and operating costs, and longest history for large continuous disinfection operations. Chlorine is a strong oxidizer.
Brita filters remove chlorine from drinking water extremely well. Chlorine is one of the first contaminants Brita targeted when they developed their filtration systems.
Brita filters use activated carbon to remove chlorine from water. Activated carbon works very well at removing this impurity. Brita uses coconut shell carbon which is especially good at removing this disinfectant.
Brita makes four different types of filter systems and sells three different filters. The following table summarizes the chlorine removal performance of each filter sold by Brita.
| Brita Filter | Treatment Rating | NSF Certification |
| Standard filter | Reduces chlorine | Not certified |
| LongLast+ filter | Removes 97.4% of chlorine | NSF certified to reduce chlorine |
| Stream filter | Reduces chlorine | Not certified |
| Bottle filter | Reduces chlorine | Not certified |
| Faucet filter | Removes 97.5% of chlorine | NSF certified to reduce chlorine |
Read my article – Do Brita Filters Remove Chlorine? A Comprehensive Look. I have another article Do Brita Filters Really Make Water Taste Better.
2 – Lead removal with Brita filters
Lead can be found in many products such as paints, plumbing fixtures or pipes. It enters our drinking water by corrosion of household plumbing systems, discharge from industrial pollution and erosion of soil deposits.
Lead exposure causes behavioral issues and learning disabilities in children. Children under the age of six are most at risk because this is when their brains are still developing.
The maximum contaminant level goal (MCLG) for lead is 0 milligrams per liter (mg/L). The MCLG is set by the US EPA. It is highest contaminant concentration in drinking water where there is no expected risk to health.
Lead can be removed from drinking water using ion exchange resin. Brita uses this treatment media in some of its filters to remove lead.
The following Brita filters can remove lead:
- Brita LongLast+ filter
- Brita faucet filter
Brita makes four different types of filter systems and sells three different filters. The following table summarizes the lead removal performance of each filter system and filter sold by Brita.
| Brita Filter | Treatment Rating | NSF Certification |
| Standard filter | Does not remove lead | Not certified |
| LongLast+ filter | Removes 99.5% of lead | NSF 53 certified to reduce lead |
| Stream filter | Does not remove lead | Not certified |
| Bottle filter | Does not remove lead | Not certified |
| Faucet filter | Removes 99.3% of lead | NSF 53 certified to reduce lead |
Read my article – Brita Filters: Which models remove lead from drinking water?
3 – Benzene removal with Brita filters
Benzene is a clear, colorless volatile organic compound (VOC). It is very flammable. It is found in gasoline, cigarette smoke, and crude oil.
Benzene can contaminate drinking water from industrial discharges, leaking underground storage tanks, and landfills.
Benzene is a known human carcinogen. It also causes anemia, reduced blood platelet levels, and liver damage.
The drinking water standard (MCL) for benzene is 5 parts per billion (ppb). Several state health agencies have set lower drinking water limits for this compound.
Benzene can be removed from water using activated carbon. Brita uses coconut shell carbon, which is especially good at removing this VOC.
The following table summarizes the benzene removal performance of each filter sold by Brita.
| Brita Filter | Treatment Rating | NSF Certification |
| Standard filter | Removes some benzene | Not certified |
| LongLast+ filter | Removes 93.5% of benzene | NSF certified to reduce benzene |
| Stream filter | Removes some benzene | Not certified |
| Bottle filter | Removes some benzene | Not certified |
| Faucet filter | Removes 96.6% of benzene | NSF certified to reduce benzene |
4 – Particulate and turbidity removal with Brita filters
Turbidity is a measure of the cloudiness in water, and it’s used to indicate how well your filter keeps you safe from disease-causing microorganisms like viruses, parasites or bacteria. Many experts believe that increased turbidity is linked to an increase of dangerous microorganisms, such as viruses, parasites and certain types of bacteria. These organisms may lead to symptoms like nausea, cramps, diarrhea, and headaches.
The primary source of turbidity in drinking water is runoff from agricultural and industrial activity. It is especially noticeable following a rainstorm.
There is no drinking water standard for turbidity.
The removal of particulates and turbidity is an important function of drinking water filters. Brita’s line of filtration products effectively removes these solids because of the particulate filter.
The following table summarizes the particulate and turbidity removal performance of each filter sold by Brita.
| Brita Filter | Treatment Rating | NSF Certification |
| Standard filter | Removes some particulates | Not certified |
| LongLast+ filter | Removes 99.6% of particulates | NSF 42 certified to reduce particulates |
| Stream filter | Removes some particulates | Not certified |
| Bottle filter | Removes some particulates | Not certified |
| Faucet filter | Removes 99.6% of particulates | NSF 42 certified to reduce particulates |
5 – Mercury removal with Brita filters
Mercury is a toxic metal found in many different places around the environment. It can come from refinery and factory pollution, coal burning or landfill leachate. Half of the mercury used in electrical products like dry-cell batteries, fluorescent light bulbs, switches, and other control equipment.
Mercury enters our drinking water supplies through natural deposits, discharge from refineries and factories, and runoff from landfills and croplands.
The primary health effect of mercury exposure is kidney damage. The national drinking water standard (MCL) for mercury is 2 parts per billion (ppb).
Carbon adsorption is quite effective at removing mercury from mercury. Brita uses coconut shell carbon filtration technology in all of its filters. Brita filters remove mercury from drinking water very well.
The following table summarizes the mercury removal performance of each filter sold by Brita.
| Brita Filter | Treatment Rating | NSF Certification |
| Standard filter | Does not remove mercury | Not certified |
| LongLast+ filter | Removes 95.9% of mercury | NSF 53 certified to reduce mercury |
| Stream filter | Does not remove mercury | Not certified |
| Bottle filter | Does not remove mercury | Not certified |
| Faucet filter | Does not remove mercury | Not certified |
6 – Cadmium removal with Brita filters
Cadmium is a metal used in the manufacturing of steel and plastic. It is released from corrosion, runoff from industrial processes like mining or oil drilling, waste batteries, and fertilizer contamination.
Cadmium is known to cause kidney damage, and long-term exposure has been linked to cancer. The EPA has set the maximum contaminant level goal for cadmium in water at 0.005 mg/L.
Cadmium enters our drinking water through corrosion of galvanized pipes, erosion of natural deposits, discharge from metal refineries, and runoff from waste batteries and paints.
Ion exchange is a very effective treatment technology for removing cadmium from drinking water. Several Brita filters use ion exchange resin to remove cadmium from water.
The following table summarizes the cadmium removal performance of each filter sold by Brita.
| Brita Filter | Treatment Rating | NSF Certification |
| Standard filter | Does not remove cadmium | Not certified |
| LongLast+ filter | Removes 99.2% of cadmium | NSF 53 certified to reduce cadmium |
| Stream filter | Does not remove cadmium | Not certified |
| Bottle filter | Does not remove cadmium | Not certified |
| Faucet filter | Does not remove cadmium | Not certified |
7 – Copper removal with Brita filters
Copper is a common metal found in many plumbing materials. It is often used in pipes and fixtures because it is durable and has a long lifespan. While copper is not considered a health hazard at low levels, it can cause an unpleasant taste in your water. High levels of copper can be toxic and cause health problems.
Copper can enter drinking water by coming from natural deposits or corrosion on household pipes.
Some people who consume water with excessive copper levels might develop gastrointestinal problems and liver or kidney damage.
The national public health goal for copper in drinking water is 1.3 milligrams per liter (ppm). The Copper is covered by the Treatment Technique rule which requires systems to monitor drinking water at customer taps. A water system must take specific actions to control corrosion if more than 10% of the customer taps contain copper concentrations that exceed 1.3 ppm.
Copper can be effectively removed from water using ion exchange resin. Several Brita filters incorporate ion exchange resin and can effectively remove copper from drinking water.
The following table summarizes the copper removal performance of each filter sold by Brita.
| Brita Filter | Treatment Rating | NSF Certification |
| Standard filter | Does not remove copper | Not certified |
| LongLast+ filter | Removes some copper | Not certified |
| Stream filter | Removes some copper | Not certified |
| Bottle filter | Removes some copper | Not certified |
| Faucet filter | Removes some copper | Not certified |
8 – Zinc removal with Brita filters
Zinc is a metal that is used to galvanize steel and iron to prevent rusting. Zinc is used to make brass and bronze by alloying it with copper, as well as other metals.
Zinc contaminates our drinking water primarily from leaching of galvanized water pipes, but can also come from mining and industrial wastes. Although zinc is an essential nutrient for our health, too much zinc can be toxic.
There is no national drinking water standard for zinc. The EPA established a secondary water quality standard of 5 ppm for zinc.
Ion exchange resin is very effective at removing copper from water. Several Brita filters incorporate ion exchange resin and can effectively remove zinc from drinking water.
The following table summarizes the copper removal performance of each filter sold by Brita.
| Brita Filter | Treatment Rating | NSF Certification |
| Standard filter | Does not remove zinc | Not certified |
| LongLast+ filter | Removes some zinc | Not certified |
| Stream filter | Removes some zinc | Not certified |
| Bottle filter | Removes some zinc | Not certified |
| Faucet filter | Removes some zinc | Not certified |
9 – Pharmaceuticals removal with Brita filters
Although you may not be able to see it, small amounts of prescription and over the counter (OTC) drugs are present in our drinking water. Examples of these pharmaceuticals include antibiotics, hormones, mood stabilizers, and other pharmaceuticals.
One of the most common ways that pharmaceuticals get into our water supply is when people flush prescription or over the counter medications down toilets. You may think wastewater treatment plants would take care of this situation, but they do not have any effect on these substances passing through surface waters.
Drinking water with pharmaceuticals is undesirable because of the potential side effects these drugs have. For example, ingesting hormones when you don’t need them can lead to health problems.
Depending on which chemical is involved, pharmaceuticals can be removed from water using activated carbon and ion exchange resin. Brita filters use these treatment technologies.
Several Brita filters have been tested and shown to remove 99% of ibuprofen, atenolol, progesterone, and estrone from water. The following table summarizes the pharmaceutical removal performance of each filter sold by Brita.
10 – 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene removal with Brita filters
1,2,4-trichlorobenzene is an environmental toxin that comes from the textile finishing factories and industrial chemical manufacturing. It is primarily used as a dye carrier, but it can also be found in herbicides, solvents, wood treatments, and a pesticide used against termites.
The primary way this contaminant gets into our drinking water is from textile finishing factories.
Health effects from 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene include changes in adrenal glands, liver, and kidney function. Short-term exposure to high levels of the contaminant can lead to dizziness, headaches, and nausea. Long-term exposure has been linked with an increased risk for cancer.
The EPA established a MCLG of 70 ppb for 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene. This is the highest level that can be consumed without adverse effects.
Activated carbon works very well to remove 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene from water, and all Brita filters use carbon filtration. As a result, all Brita filters remove 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene from drinking water.
11 – Asbestos removal with Brita filters
Asbestos is found in a wide variety of products, including:
- building products
- roof shingles
- tiles
- textured paint
- stove-top pads
- some vinyl floor tiles
- insulation materials and gaskets
There are two primary sources of asbestos in our drinking water.:
- the decay of asbestos cement in water mains
- the erosion of asbestos natural deposits
Asbestos causes several negative health effects including:
- lung cancer
- mesothelioma
- askestosis
The EPA established a MCLG of 7 million fibers per liter for asbestos.
Asbestos fibers can be removed from water with particle filters. All Brita filters include at least one type of particle filters. Brita filters can remove asbestos fibers from water. Not all filters are certified for asbestos removal
12 – Pesticide and herbicide removal with Brita filters
Pesticides and herbicides are widely used throughout the United States. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), these chemicals are designed to kill pests, weeds, and other unwanted vegetation.
While pesticides and herbicides can be effective at killing unwanted plants and insects, they can also be harmful to human health. Exposure to these chemicals has been linked to a variety of health problems, including cancer, reproductive damage, and endocrine disruption.
Runoff from these chemicals can end up in our drinking water, where they can be harmful to our health.
Many pesticides and herbicides can be removed using activated carbon. Brita filters all use carbon filtration to remove pesticides and herbicides from water.
The following table summarizes the herbicide and pesticide removal performance of each filter sold by Brita.
| Brita Filter | Treatment Rating | NSF Certification |
| Standard filter | Removes some Pesticides and herbicides | Not certified |
| LongLast+ filter | Removes some Pesticides and herbicides | Not certified |
| Stream filter | Removes some Pesticides and herbicides | Not certified |
| Bottle filter | Removes some Pesticides and herbicides | Not certified |
| Faucet filter | Alachlor: >97.5% Atrazine: >95% Endrin: >97% Lindane: >99% Methoxychlor: 00.7% Simazine: 87% Toxaphene: 93.6% | NSF 53 certified to reduce listed pesticides and herbicides |
Read my article Do Brita Filters Remove Glyphosate (Round Up) from Water
13 – Atrazine removal with Brita filters
Atrazine is a widely used herbicide for control of broadleaf and grassy weeds. As of 1993, its uses were greatly restricted due to the discovery that it can cause adverse reproductive effects as well as toxicity on immune system cells.
Drinking water contamination comes primarily from herbicide used on row crops such as corn, sugarcane and sorghum.
Atrazine causes harm to the cardiovascular system and can lead to reproductive difficulties.
The drinking water standard for atrazine is 3 parts per billion (ppb).
The following table summarizes the atrazine removal performance of each filter sold by Brita.
| Brita Filter | Treatment Rating | NSF Certification |
| Standard filter | Does not remove atrazene | Not certified |
| LongLast+ filter | Removes some atrazene | Not certified |
| Stream filter | Removes some atrazene | Not certified |
| Bottle filter | Removes some atrazene | Not certified |
| Faucet filter | Removes >95% atrazene | NSF 53 certified to reduce atrazene |
14 – Total trihalomethanes (TTHM) removal with Brita filters
Trihalomethanes (THMs) are four disinfection byproducts: chloroform, bromodichloromethane, dibromochloromethane, and bromoform.
Bromoform is formed when chlorine or other disinfectants are used to treat drinking water. Research on animals suggests that chronic oral exposure to bromoform can have negative effects on the liver, kidney, and central nervous system.
Chloroform is a disinfection byproduct that forms when water is treated with chlorine. It is a suspected carcinogen that can harm the eyes, skin, liver, kidneys, and nervous system.
Bromodichloromethane is created when chlorine and other disinfectants react with organic material in water. It is a suspected carcinogen that may cause liver damage, kidney damage, and decreases in immune response.
Dibromochloromethane is formed when chlorine or other disinfectants are used to treat drinking water. It can damage the liver and kidneys and affect the brain.
The USEPA has set an MCL for TTHM of 80 parts per billion (ppb)
The following table summarizes the trihalomethanes removal performance of each filter sold by Brita.
| Brita Filter | Treatment Rating | NSF Certification |
| Standard filter | Removes some THMs | Not certified |
| LongLast+ filter | Removes some THMs | Not certified |
| Stream filter | Removes some THMs | Not certified |
| Bottle filter | Removes some THMs | Not certified |
| Faucet filter | Removes 98.7% THMs | NSF 53 certified to reduce THMs |
Brita Filter Performance – Testing Results
As part of the NSF certification process, the Brita LongLast, LongLast+, and faucet filters were tested to see how well they removed lead, mercury, and several other contaminants. The testing was conducted using high concentrations of these compounds and the results were compared to the EPA’s drinking water standards (also known as the Maximum Contaminant Levels).
1 – Brita LongLast filter performance results
The Brita LongLast filters are certified to NSF/ANSI standard 53 (health effects), standard 401 (emerging compounds/incidental contaminants), and standard 42 (aesthetic effects).
The following table lists the contaminant reduction for the Brita LongLast filter and all of the contaminants it was tested for (NSF/ANSI Standard 53 – Health Effects).
| Substance | Overall Percent Reduction | Drinking Water Standard |
| Lead pH 6.5 | 99.5% | 10 ppb |
| Lead pH 8.5 | 99.6% | 10 ppb |
| Mercury pH 6.5 | 95.5% | 2 ppb |
| Mercury pH 8.5 | 93.4% | 2 ppb |
| Cadmium pH 6.5 | 97.4% | 5 ppb |
| Cadmium pH 8.5 | 99.2% | 5 ppb |
| Asbestos | >99% | 99%* |
| Benzene | 93.5% | 5 ppb |
Here is the table for Brita LongLast performance with emerging contaminants (NSF/ANSI Standard 401 – Emerging Compounds/Incidental Contaminants)
| Substance | Overall Percent Reduction | Drinking Water Standard |
| Bisphenol A | 95.5% | 300 ppt |
| Estrone | 96.4% | 20 ppt |
| Ibuprofen | 94.9% | 60 ppt |
| Naproxen | 96.4% | 20 ppt |
| Nonyl phenol | 93.5% | 200 ppt |
The following table summarizes the LongLast performance with qualitative contaminants (NSF/ANSI standard 42 – aesthetic effects).
| Substance | Overall Percent Reduction | Drinking Water Standard |
| Chlorine (taste & Odor) | 97.4% | 50% (NSF standard) |
| Particulate Reduction (Class I) | 99.6% | 85% (NSF standard) |
2 – Brita LongLast+ filter performance results
The Brita LongLast+ filters are certified to NSF/ANSI standard 53 (health effects), standard 401 (emerging compounds/incidental contaminants), and standard 42 (aesthetic effects).
The following table lists the contaminant reduction for the Brita LongLast+ filter and all of the contaminants it was tested for (NSF/ANSI Standard 53 – Health Effects).
| Substance | Overall Percent Reduction | Drinking Water Standard |
| Lead (pH 6.5) | 99.5% | 10 ppb |
| Lead (pH 8.5) | 99.6% | 10 ppb |
| Mercury (pH 6.5) | 95.5% | 2 ppb |
| Mercury (pH 8.5) | 95.9% | 2 ppb |
| Cadmium (pH 6.5) | 96.9% | 5 ppb |
| Cadmium (pH 8.5) | 99.2% | 5 ppb |
| Asbestos | >99% | 99% (NSF standard) |
| 2,4-D | 85.5% | 70 ppb |
| Atrazine | 99.3% | 3 ppb |
| Benzene | 93.5% | 5 ppb |
| Endrin | 98.7% | 2 ppb |
| Ethylbenzene | 99.0% | 700 ppb |
| Carbon Tetrachloride | 91.2% | 5 ppb |
| P-Dichlorobenzene | 98.2% | 75 ppb |
| Simazine | 98.4% | 4 ppb |
| Tetrachloroethylene | 96.1% | 5 ppb |
Here is the table for Brita LongLast+ performance with emerging contaminants (NSF/ANSI Standard 401 – Emerging Compounds/Incidental Contaminants)
| Substance | Overall Percent Reduction | Drinking Water Standard |
| Atenolol | >95% | 30 ppt |
| Bisphenol A | 95.5% | 300 ppt |
| Carbamazepine | >96% | 200 ppt |
| DEET | 98.0% | 200 ppt |
| Estrone | 96.4% | 20 ppt |
| Ibuprofen | 94.9% | 60 ppt |
| Linuron | >93% | 20 ppt |
| Meprobamate | >94% | 60 ppt |
| Metolachlor | >94% | 200 ppt |
| Naproxen | 96.4% | 20 ppt |
| Nonyl phenol | 93.5% | 200 ppt |
| Phenytoin | >95% | 30 ppt |
| TCEP | 99% | 700 ppt |
| TCPP | >99% | 700 ppt |
| Trimethoprim | >96% | 20 ppt |
The following table summarizes the LongLast+ performance with qualitative contaminants (NSF/ANSI standard 42 – aesthetic effects).
| Substance | Overall Percent Reduction | Drinking Water Standard |
| Chlorine | 97.4% | 50% (NSF standard) |
| Particulate Reduction (Class I) | 99.6% | 85% (NSF standard) |
3 – Brita faucet filter performance results
The Brita faucet filters are certified to NSF/ANSI standard 53 (health effects) and standard 42 (aesthetic effects).
The following table lists the contaminant reduction for the Brita faucet filter and all of the contaminants it was tested for (NSF/ANSI Standard 53 – Health Effects).
| Substance | Overall Percent Reduction | Drinking Water Standard |
| Asbestos | >99% | 99% (NSF standard) |
| Lead | >99.3% | 10 ppb |
| Lead | >99.3% | 110 ppb |
| Cysts | >99.99% | 99.95% (NSF standard) |
| Alachlor | >97.5% | 2 ppb |
| Atrazine | >95% | 3 ppb |
| Benzene | >96.6% | 5 ppb |
| Carbofuran | >98.7% | 40 ppb |
| Carbon tetrachloride | >96.5% | 5 ppb |
| Chlordane | 98.9% | 2 ppb |
| Chlorobenzene | 99.9% | 0.1 ppm |
| o-Dichlorobenzene | >99.9% | 0.6 ppm |
| 2,4-D | 99.9% | 70 ppb |
| Endrin | >97% | 2 ppb |
| Ethylbenzene | 99.9% | 0.7 ppm |
| Lindane | >99% | 0.2 ppb |
| Methoxychlor | 99.7% | 40 ppb |
| Simazine | 87% | 4 ppb |
| Styrene | >99.9% | 0.1 ppm |
| Tetrachloroethylene | >96.9% | 5 ppb |
| Toluene | >99.9% | 1 ppm |
| Toxaphene | >93.6% | 3 ppb |
| Trichloroethylene | >99.8% | 5 ppb |
| TTHM | 98.7% | 80 ppb |
| Turbidity | 99% | 0.5 NTU (NSF standard) |
| VOC | 99.7% | N.A. |
The following table summarizes the Brita faucet filter performance with qualitative contaminants (NSF/ANSI standard 42 – aesthetic effects).
| Substance | Overall Percent Reduction | Drinking Water Standard |
| Chlorine (taste & Odor) | 97.5% | 50% (NSF standard) |
| Particulate Reduction (Class I) | 99.7% | 85% (NSF standard) |
Contaminants That Brita Only Partially Removes from Water
Brita is very effective at removing taste and odor compounds from water. It is also able to remove some dangerous contaminants such as lead and asbestos. For many of these compounds, Brita filters have been independently certified by NSF.
However, for some contaminants, Brita filters are not able to remove 100% of them. In these instances, it is not recommended that you use a Brita filter as the primary method of purifying your drinking water.
Some of the contaminants that Brita only partially removes include:
Related articles on Brita’s performance with contaminants:
New Brita Filter Removes 11 PFAS Compounds – Purefast
NSF Certification
The National Sanitation Foundation (NSF) is an independent, nonprofit organization that tests and certifies products to ensure they meet strict public health standards. Some Brita filters are certified by the NSF to remove a wide range of contaminants from drinking water, including lead, chlorine, and asbestos.
To be certified by the NSF, a product must go through a rigorous testing and certification process. The NSF tests products to ensure they meet strict performance standards for the removal of specific contaminants.
The NSF also requires manufacturers to have their products independently tested by an accredited laboratory to verify that the product meets the NSF’s performance standards. This ensures that Brita filters continue to remove contaminants effectively over time.
Value of NSF certification
The primary benefit of NSF certification is that it provides peace of mind to consumers that a product meets strict public health standards. This third-party testing agency verifies all of the claims made by the manufacturers such as their ability to remove contaminants from water.
When you see the NSF logo on a Brita filter, you can be confident that the filter has been independently tested and certified to reduce the contaminants listed by NSF.
The NSF certification process is very rigorous and provides assurance to consumers that a product will perform as advertised.
Which Brita filters have NSF certification
The following Brita filters have been evaluated by NSF to meet NSF/ANSI standards.
For NSF certifications that indicate the filter can reduce volatile organic compounds (VOCs), the following chemicals are included:
- alachlor
- atrazine
- benzene
- carbofuran
- carbon tetrachloride
- chlorobenzene
- chloropicrin
- 2,4-D
- dibromochloropropane (DBCP)
- o-dichlorobenzene
- p-dichlorobenzene
- 1,2-dichloroethane
- 1,1-dichloroethylene
- cis-1,2-dichloroethylene
- trans-1,2-dichloroethylene
- 1,2-dichloropropane
- cis-1,3-dichloropropylene
- dinoseb
- endrin
- ethylbenzene
- ethylene dibromide (EDB)
- haloacetonitriles
- bromochloroacetonitrile
- dibromoacetonitrile
- dichloroacetonitrile
- trichloroacetonitrile
- haloketones
- 1,1-dichloro-2-propanone
- 1,1,1-trichloro-2-propanone
- heptachlor
- heptachlor epoxide
- hexachlorobutadiene
- hexachlorocyclopentadiene
- lindane
- methoxychlor
- pentachlorophenol
- simazine
- styrene
- 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane
- tetrachloroethylene
- toluene
- 2,4,5-TP(silvex)
- tribromoacetic acid
- 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene
- 1,1,1-trichloroethane
- 1,1,2-trichloroethane
- trichloroethylene
- trihalomethanes (TTHM)
- bromodichloromethane
- bromoform
- chlorodibromomethane
- chloroform
- xylenes
FAQs
Do Brita filters remove Microplastics?
Brita filters remove microplastics very well. The particulate filter that is built into every Brita filter unit can remove more than 99.99% of the microplastics in your water.
Read my article on Brita filters and microplastics.
Do Brita filters remove bacteria and viruses?
Brita filters do not remove bacteria or viruses. Brita very clearly notes on all of their filters that they can’t be used to remove bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens from drinking water.
Is Brita filter better than bottled water?
Most bottled water is just tap water that has been filtered. The most common treatment technology used on bottled water is reverse osmosis. Some bottled waters are also further treated with carbon filtration, UV light, and ozone.
Brita filters use particle filtration, activated carbon, and ion exchange resin. While this level of treatment is good, it is not as good as the RO treatment used on bottled water.
Final Take on Brita Filters
A Brita filter is a simple and effective way to remove impurities from your drinking water. The activated carbon filtration system removes chlorine, lead, benzene, and other particulates from the water. Additionally, the ion exchange resin removes heavy metals such as mercury, cadmium, and copper.
Brita also filters out harmful chemicals like pesticides, herbicides, and pharmaceuticals. If you are concerned about the quality of your drinking water, consider investing in a Brita filter pitcher or faucet mount filter. These devices will provide you with clean, safe water for years to come.

